


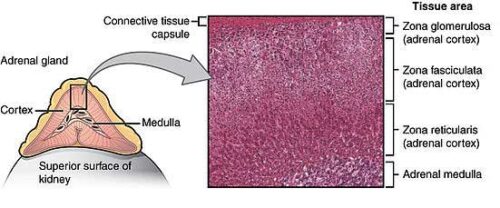
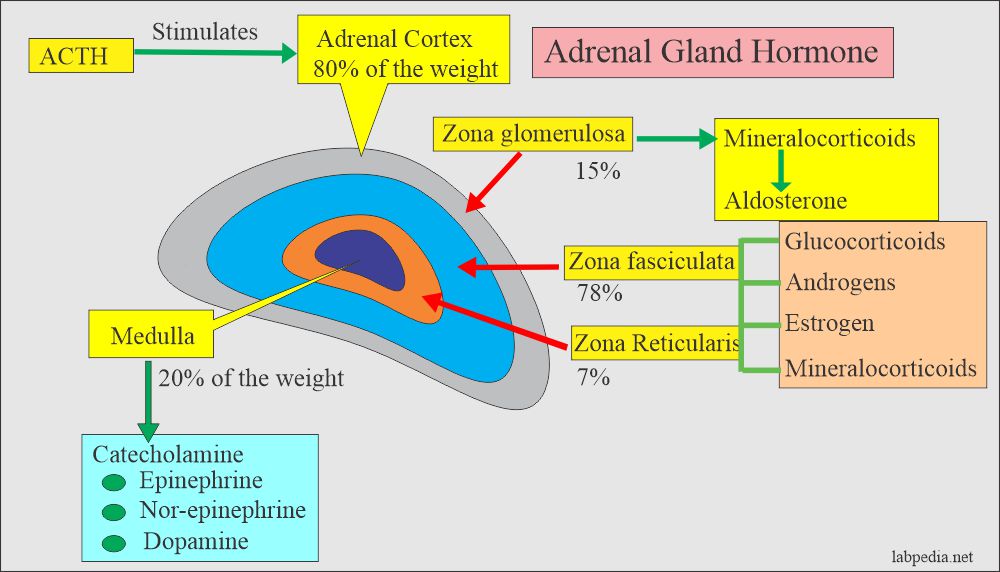
Both classes of adrenergic receptors are expressed in most tissues. Additionally, although norepinephrine will activate both subtypes of beta receptors, epinephrine will activate only the beta 1 receptors. There, both the alpha 1 and alpha 2 receptors are located postsynaptically. This is in contrast to the alpha adrenergic receptors within the central nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system, alpha 1 receptors are located postsynaptically and mediate excitatory effects while the alpha 2 receptors are presynaptic autoreceptors that temper norepinephrine release. Both classes of adrenergic receptors are G-protein coupled and the ligand–receptor complex ultimately determines the signal transduction pathway and consequent activation or deactivation of the cell.Įpinephrine and norepinephrine bind to and activate both alpha receptors with different affinities and potencies. The adrenergic receptors come in two classes of receptor: alpha (1, 2) and beta (1, 2), each with two principal subtypes. 21 The catecholamines then bind to adrenergic receptors and further activate the sympathetic response. Upon receiving cholinergic input from the sympathetic system via the splanchnic nerves, the chromaffin cells from the adrenal medulla release stored epinephrine and norepinephrine. It is divided into the cortex (adrenocortical path), where cortisol and other steroid hormones are synthesized, and the adrenal medulla (adrenomedullary path). The adrenal gland serves as the peripheral endocrine component of the ANS. In human beings ≥ 90% of pheochromocytomas arise from the adrenal medulla and are linked with a clinical syndrome termed multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN).ĭerrick Lonsdale, Chandler Marrs, in Thiamine Deficiency Disease, Dysautonomia, and High Calorie Malnutrition, 2017 Adrenergic Receptors and Response Due to the catecholamines produced by these masses, these patients may experience marked (occasionally fatal) fluctuations in blood pressure and arrhythmias during the peri-operative period.
If metastasis is not identified during workup, patients are stabilized with an alpha 1-antagonist before careful surgical excision.
Usually solitary, slow-growing masses, they locally invade the caudal vena cava and can metastasize to the liver and regional lymph nodes. Most often seen in dogs and cows, and occasionally in horses, pheochromocytomas are most commonly tumors of chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla (or less commonly paragangliomas) that secrete excess catecholamines-epinephrine and/or norepinephrine.Ĭlinical signs are usually variable and nonspecific, including PU/PD, increased panting, lethargy, weakness/collapse, anorexia, vomiting, and diarrhea. Pheochromocytomas are the most common, though still rare, tumor of the adrenal medulla.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
